Zonulin, Leaky Gut and Autoimmune Diseases
Zonulin, Leaky Gut and Autoimmune Disease
What is Zonulin?
Simply put, Zonulin is a protein that that opens the tight junctions and increases paracellular permeability, inducing what we call ‘leaky gut’ syndrome. Zonulin is made in the gastrointestinal mucosa more specifically, zonulin is made in the intestinal enterocytes and liver cells.
Zonulin plays a major role as a regulator of intestinal barrier function. Elevated levels of zonulin are a biological door to inflammation, autoimmunity and yes, certain types of cancer have been associated with elevated levels of zonulin.
Zonulin was discovered in 2000 by Alessio Fasano, is a protein secreted by the cells in the gut wall that stimulate the opening of gaps between cells in the intestinal barrier. Zonulin has been implicated in the pathogenesis of several disease processes such as celiac disease, diabetes mellitus type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. Those who suffer from these diseases have shown increased levels of zonulin and an increase in intestinal permeability because zonulin causes a breakdown of the tight intracellular junctions between the epithelial cells of the gut wall. Of note, research has shown the effects of zonulin are reversable.
Symptoms Associated with Leaky Gut Syndrome
Leaky gut syndrome has been linked to myriad rad of health issues that have a direct affect on the gut (or is it the other way around). Joint pain, rosacea, eczema, anxiety and hormon imbalances have been associate with leaky gut syndrome.
Some GI indicators of leaky gut syndrome may be, but not limited to:
A burning feeling in your gut (think ulcer)
Painful indigestion – GERD
Diarrhea
Bloating
Gassy
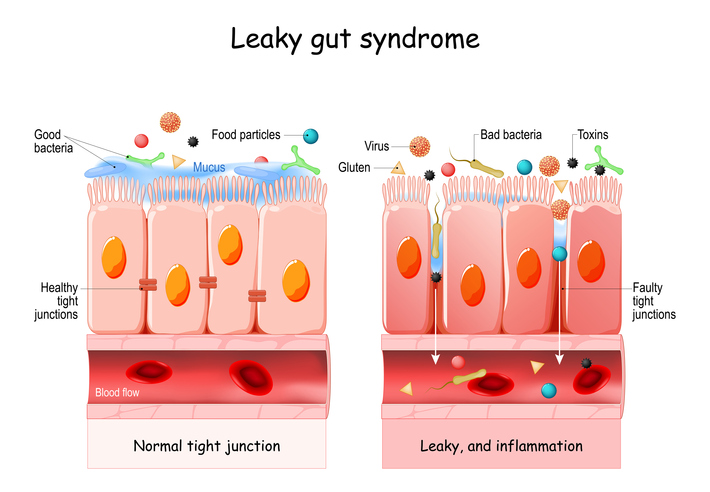
What are Tight Junctions
The paracellular (Paracellular transport is the transport of ions and molecules) that occurs in between cells, passing through an intercellular pathway. Tight junctions are found between the intestinal epithelial cells and play a crucial role creating a protective mucosal barrier in the gut while regulating the functional condition of the paracellular pathway.
The tight junction (TJ) create a protective barrier for both the passage of ions and molecules through the paracellular pathway. Basically, tight junctions are the gate keepers from letting molecules slip in between epithelial cells in the gut.
Zonulin and the Immune System
With 90% of immune system is in the GI tract, leaky gut wreaks havoc in the body, weakening immunity and causing widespread problems. What happens in GI track doesn’t just stay in the gut. In the case of leaky gut, molecules and protein particles escape the GI track and invade the circulatory system. This process happens over and over again, stimulating an immune response which leads to autoimmune and inflammatory disorders. Leaky gut and lead to chronic or recurring infections.
What Elevated Levels of Zonulin Could Indicate
Elevated levels of zonulin are associated with increased intestinal permeability (Leaky Gut) because it induces breakdown of the tight intercellular junctions between epithelial cells and toxins can slip from the gut into the blood stream inducing all kinds of health issues, such as various cancers, SIBO, Diabetes, and other inflammatory processes.
Factors that can stimulate an increase in Zonulin
• Nutrients: glucose, amino acids, mid- chain free fatty acids, oligosaccharides
• Bacterial Toxins: Cholera, Clostridium, Lipopolysaccharides
• Infections: Campylobacter, Rotavirus, Giardia
• Stress Hormone: Corticotropin- Releasing Hormone (CRH)
• Cytokines: Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha, Interferon – y, IL4.
• Medications: Aspirin, Non-Steroidal Anti-inflammatory medications
• Irritants / Toxics: Alcohol, Carrageen, Dextrin Sulfate
• Food Toxins: lectins, potatoes, eggplant, gliadin fragments, wheat, dairy products, legumes, nuts, and seeds
• Injury: Burns to the skin, heart failure, fracture
• Nutritional Deficiency’s: Vitamin A, Zinc
• Young Age: Infants, especially premature infants
• Mast Cell Degranulation: tryptase, immune modulators, cytokines, histamine
• Disrupted Sleep: Increase in CHR alters gut motility leading to SIBO
• Oxidative Stress: Damages Mucosa
What you can do if you have elevated levels of zonulin
You can avoid foods that are known triggers of zoulin such as grains such as wheat, dairy products, legumes, nuts, and seeds. Other known dietary triggers are processed foods and white sugar.
As always, discuss your concerns with your health care provider.
How you can find out what your zonulin levels are.
You can discuss your concerns with your health care provider to find out what steps you need to take to find out what your zonulin levels are.
You can also order your own test for zonulin through CanadaGIMap.com
It is a simple process. Order your own test kit, it will be mailed directly to you.
Collect your sample and return your test kit to the lab.
It takes approximately two weeks for samples to finalize. Results will be emailed directly to you.
Click on this link to order your own zonulin test or the GI Map with zonulin.